ls command in Linux is one of the fundamental commands. If you are a Linux user then at one or some point in your journey, you will need to use the ls command.
ls command in Linux is widely used for listing and displaying information about files and directories in a directory. While the basic ls command is very easy to use, just entering ls command in the terminal but ls command provides many options to enhance your Linux experience. So whether you are a beginner exploring the world of Linux or an advanced user improving your command line skill, this blog post will get you covered.
In this blog post, I’ll discuss the ls command in detail with practical examples to make learning easier.
Table of Contents
Basics of the ls Command
ls command is a fundamental command line tool for Linux and Unix-like operating systems. Basic ls command is used for listing the files and directories, but you can use ls command to get additional information about files like file names, file permission, file modified data, file size, file owner, etc.
The basic syntax of ls command
ls [options] [file/directory]lsis the ls command itselfoptionsis the additional flag that lets you customize the output oflscommandfiles/directoryis the target files and directory
Common Options and Flags
ls commands offer a range of options and flags to customize your ls command output. In this blog post, we cover most of them. Here are the most commonly used options and flags for ls command.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
l | The long-form option. This option is used to show the long-form output of ls command. This option outputs useful information about the files and directory like owner, permission, timestamp, size, etc. |
a | The all option. This option outputs all the files, including hidden files, in a directory. |
h | The human-readable option. This option prints file-size information in a human-readable way. Instead of outputting file size in bytes, it displays file size information in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), and gigabytes (GB). |
r | The reverse option. It prints the outputs in reverse order of the ls command output. |
t | The time-based sorting option. It sorts the files and directory depending on the modified time and outputs the results. |
You can combine multiple commands to organize and show outputs in the way your need. In the next section, I’ll discuss more advanced uses of ls command.
1. Displaying Additional File Details
By default, the ls command shows only the files name, but you can use ls the command to print additional useful details about the files and directory. Here are the most commonly used options for printing additional information.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
l | This option is used to show the long-form output of the ls command. It outputs useful information about the files and directories, such as owner, permission, timestamp, size, etc. |
a | The all option. This option outputs all the files, including hidden files, in a directory. |
h | The human-readable option. This option prints file-size information in a human-readable way. Instead of outputting file size in bytes, it displays file size information in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), and gigabytes (GB). |
i | This option displays the total inode number of each file and directory. |
Differentiating Between Files and Directories
When you use ls-l command to display outputs in the long format you will see an output like this
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 8, 1 May 13 10:07 block_file
crw-r--r-- 1 root root 1, 3 May 13 10:06 character_file
drwxr-xr-x 2 ashiqur users 4096 May 13 10:06 directory
prw-r--r-- 1 ashiqur users 0 May 13 10:07 named_pipe
-rw-r--r-- 1 ashiqur users 0 May 13 10:06 regular_file.txt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 ashiqur users 27 May 13 10:04 symbolic_link -> /home/ashiqur/grub2-themes/And you may encounter a problem where you will confuse which one is a file and which is a directory. But observing the output of ls-l command, you find the different patterns for files and directories. In the output, you can see several characters where the first character of the output indicates the types of files. Where
- – Represents a regular file.
- d: Represents a directory.
- l: Represents a symbolic link.
- c: Represents a special character file.
- p: Represents a named pipe (FIFO).
- s: Represents a socket.
- b: Represents a special block file.
Example of Displaying Additional File Details
Example 1: To display files and directories in a long format with additional details
ls -l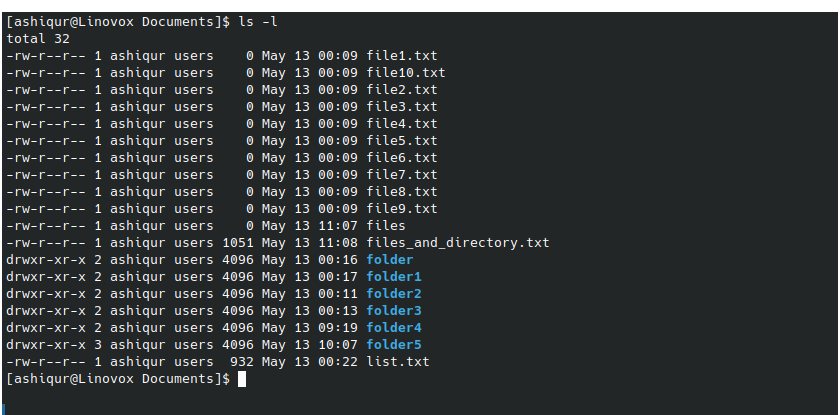
Example 2: To list all files in a long-form including hidden files
ls -la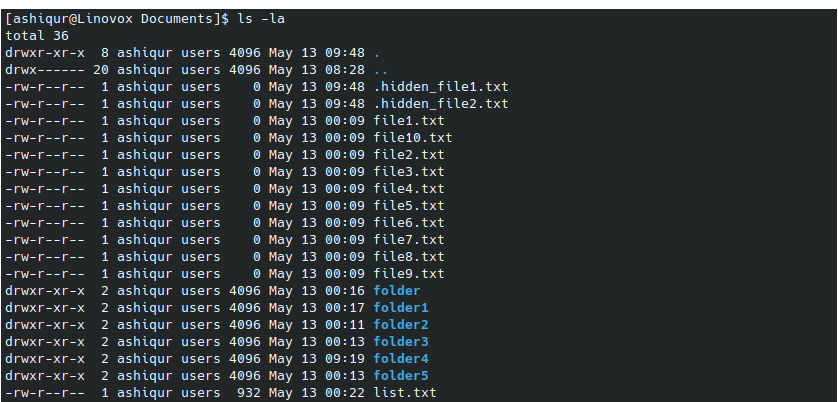
Example 3: To list files and directories in a long format with the human-readable format
ls -lh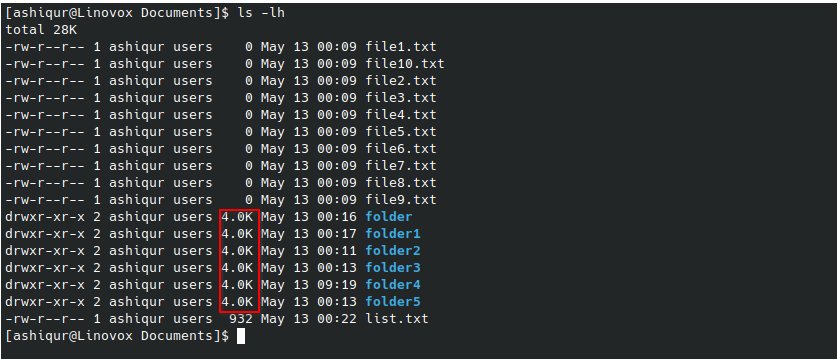
2. Sorting the Output
Sorting is arranging the files and directories in a specific order. ls command allows several sorting options to organize and present the output in useful ways. Here are sorting options for ls command.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
t | This option sorts files based on modification times of files and directories. |
S | This option sorts files based on the size of the files and prints the largest one first. |
X | This option sorts files and directories alphabetically. |
r | This option sorts files in reverse order. It prints the outputs in reverse order of the ls command output. |
Example of Sorting files
Example 1: To list files and directories sorted by modification time
ls -lt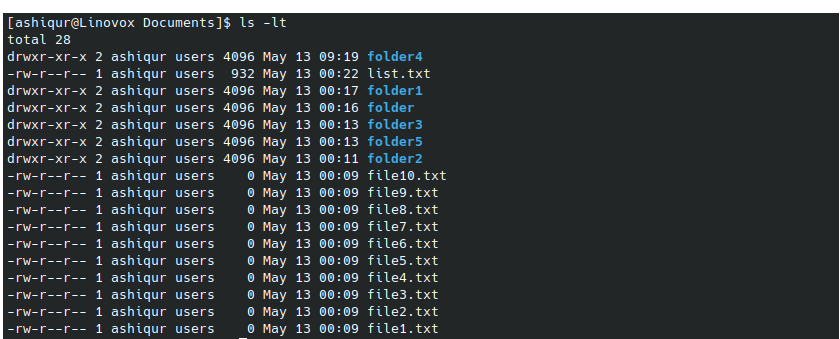
Example 2: To list files and directories sorted by modification size
ls -S
Example 3: To list files and directories sorted alphabetically
ls -X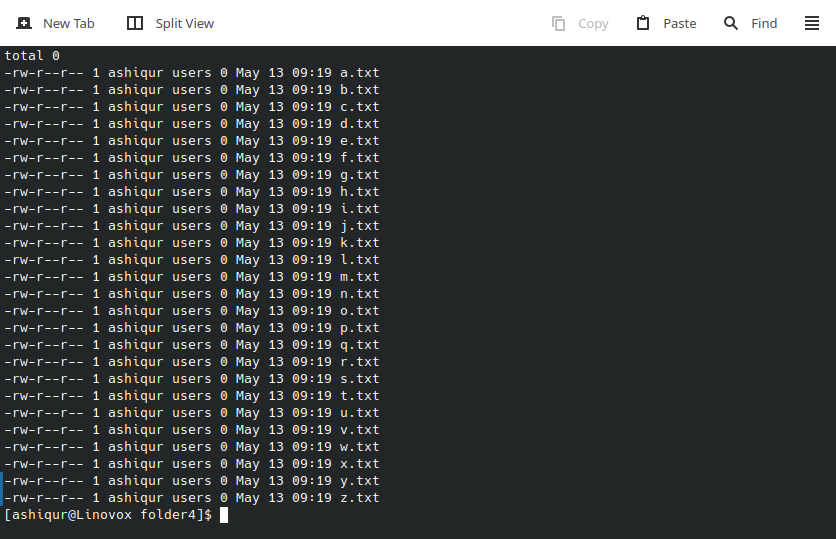
Example 4: To list the files in the reverse order
ls -r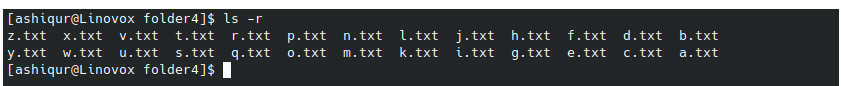
3. Filtering and Searching for Specific Entries
If you have too many files and directories in a folder, then you may find it difficult to find your targeted files or directory. You can use ls command to display the output of exactly what you are searching with the filtering and searching option of ls command.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
m | Displays the outputs separated by commas. |
R | Displays files and directories recursively, including sub-directories and their contents. |
l<pattern> | Filters the output for specific patterns and displays outputs that match the patterns. |
Example of Filtering and Searching for Specific Entries
Example 1: To list the outputs as a comma-separated list
ls -m
Example 2: To list output recursively, including the subdirectory and content inside them
ls -R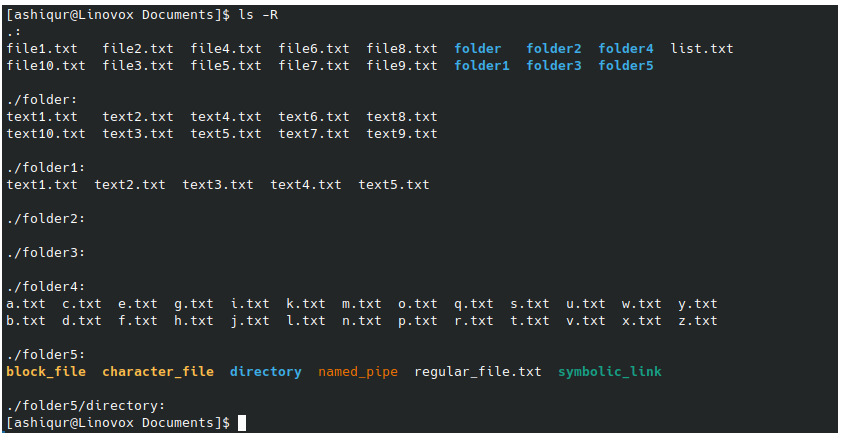
Example 3: Filter and Searching files
Suppose you have a directory where you have follwoing files
file1.txt, file10.txt, file2.txt, file3.txt, file4.txt, file5.txt, file6.txt, file7.txt, file8.txt, file9.txt, folder, folder1, folder2, folder3, folder4, folder5, list.txt.
You want to display outputs that have file in the filename. Then you can use the following command
ls -I *file*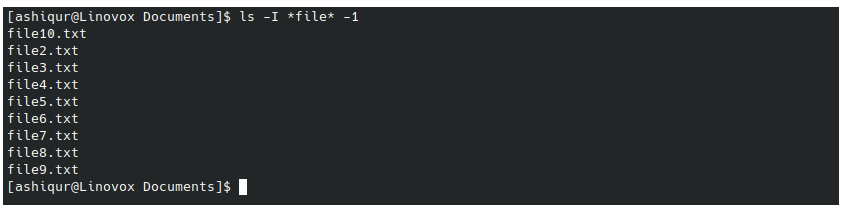
3. Customizing the Output Format
By default ls command displays a list of files and folders separated by a tab and doesn’t provide additional details. In previous examples, you have learned how to list additional information about files and directories.
You can also use ls command to customize the output format as your need. Here are options for customizing ls command output.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Force display outputs separated by new lines make reading easier. |
| -color | Display color-coded outputs and provide different colors for different file types helping distinguish different file types. |
Example of Customizing the Output Format
If you want to display output files and directory in a new line, you can use 1 option
ls -1To list color-coded output use -color option
ls --colorYou can always combine two or more outputs to customize the output of ls command.
ls -1 --color
4. Combining ls with Other Commands
The Linux terminal will allow you to use multiple commands simultaneously for more advanced use cases. You can always use ls command with another command for advanced searching and filtering.
Here are examples of combing ls command with other commands
Example 1: Piping with ls
You can pipe the output of ls command as input of another command using pipe (|). For example, if you want to search for a specific file in a directory, then you pipe all the files to the grep command to find your particular file
ls -l | grep 'keyword'This command will find the keyword from your current working directory.
Example 2: Using ls with find
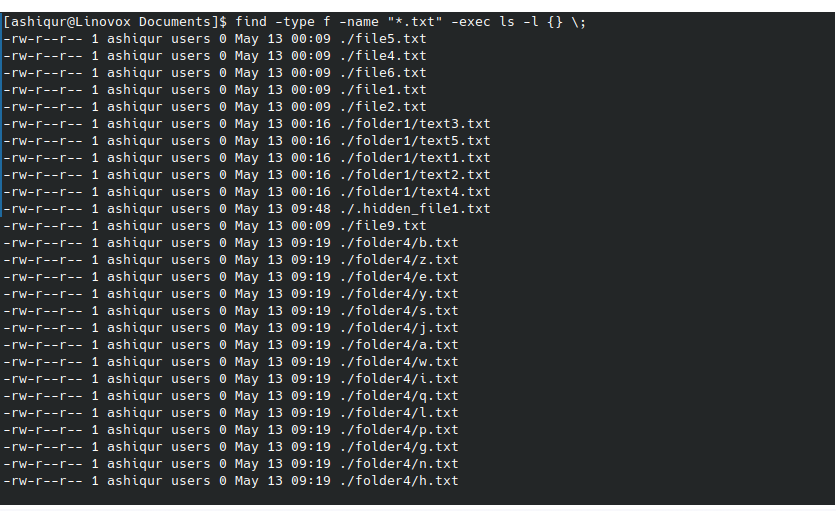
You can use ls command with find command for advanced search. The find command will find the files and directory based on your given criteria and feed to ls command to list the details output. You can see this example command
find -type f -name "*.txt" -exec ls -l {} \\;This command will display all “.txt” files with ls-l command
5. ls Command Output to a File
You can also store the result of the ls command in a file for future use. For example, if you want to keep the output of ls command tofiles_and_directory.txt file, then use the following command
ls -l -1 >files_and_directory.txtThis command will create a file and store the output in the working directory.
Conclusion
ls command is a fundamental command which Linux users and system administrators often use. But ls command gives many options in addition to the simple ls command. I have covered basic to advanced uses of ls command with examples. You can enhance your Linux skill and expertise by practicing ls command examples.




