Do you need to rename files and directories in Linux terminal without a graphical interface?
Renaming is a fundamental file operation in any operating system but without a graphical interface, it may seem daunting at first without knowledge of rename command in Linux terminal. With a simple command, you can rename files and directories in Linux.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the 3 easy ways to rename files and folders in Linux with examples and breakdowns of the command. We will also discuss the advanced options for bulk renaming.
Table of Contents
1. Rename Files Using the mv Command
The easiest way to rename files in the Linux terminal is using mv command. The mv command is widely used for moving files from one directory to another directory. We can utilize mv command to rename files. The basics syntax of mv command is
mv [options] source_file(s) target_file_or_directoryThe syntax is simple it moves source files to target files or directories. We can add options and flags for more control mv commands.
Renaming a Single File
If you need to rename a single file. It would be easy to use the following command to rename files without avoiding complexity.
mv oldfilename newfilenameThis command basically moves old files to new non existed files in the same directory which is equivalent to renaming a file. So if you are not in the same directory where the file is located. You need to navigate the target directory by using the following command in the terminal
cd /targeted_directorySuppose, you have a file named file1.txt and you want to change the file name to newfile.txt. You can use mv command as follows
mv file1.txt newfile.txtThis command will rename file1.txt to newfile.txt
Renaming Multiple Files with a Single Command
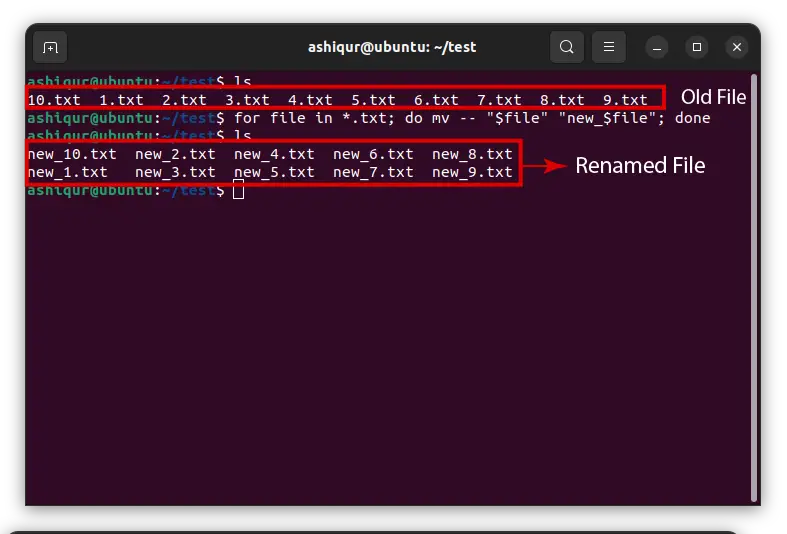
Now, If you need to rename multiple files you can rename these files with mv command we discussed above. But renaming a single file at a time is time-consuming. If you have a common pattern in the files that need to rename you can use for loop to rename multiple files with a single command.
for file in file*.txt; do mv -- "$file" "new_${file}"; doneThis is a for loop for the bash command. where
fileis the variable that holds the name of the old file namefile*.txtincludes all file that has name file in first and end with txt extension.—dash-dash is used to neglect any unexpected option and flags in the file name.- Then we use the same mv command that we used previously but with a variable in it.
Renaming a File and Moving It to a Different Directory
As you know mv command is used for moving operations and now you learn to rename files with mv command. If you have a situation when you need to perform both moving and renaming you can use a single command to do this. Open your terminal and enter the following command to do this
mv oldfilename /path/to/new/directory/newfilenameAdditionally, if you want to avoid prompts while using the mv command you can use flags -i and you want to see what mv command is doing behind the walls you can use e flag -v for this. Here we use these flags in our previous example.
mv -i -v oldfilename newfilename2. Rename Files Using Terminal File Manager
If you want to rename graphically in the Linux terminal you can do that. vifm is a file manager with a curses interface, which provides a Vim-like environment for managing objects within file systems.
To install vifm in Ubuntu/Debian-based distribution use the following command
sudo apt intall vifmTo install vifm in Arch Based distribution use the following command
sudo yay -S vifmFirst, navigate to the destination folder to use vifm file manager to rename files and enter the command
vifmyou see an interface like this
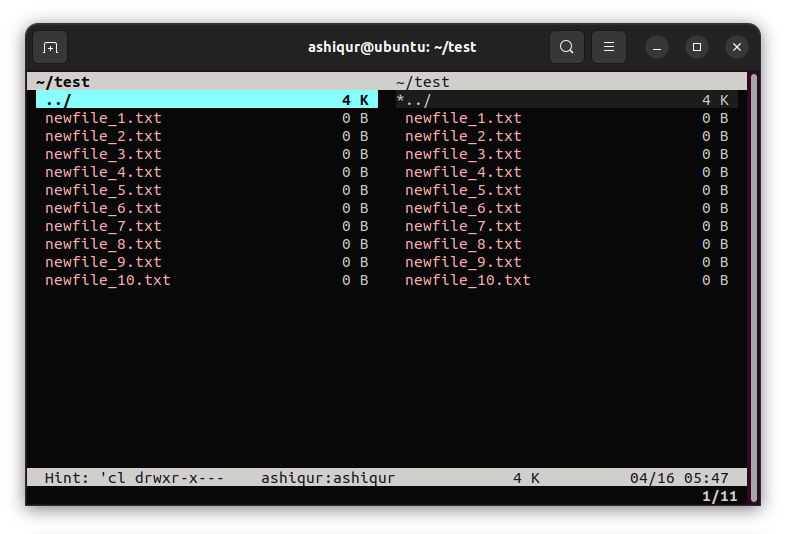
Use the Up and Down arrow keys to navigate between files. Navigate to the file you want to rename and press C key to change the file. You can see the following interface and things you can change with vifm.
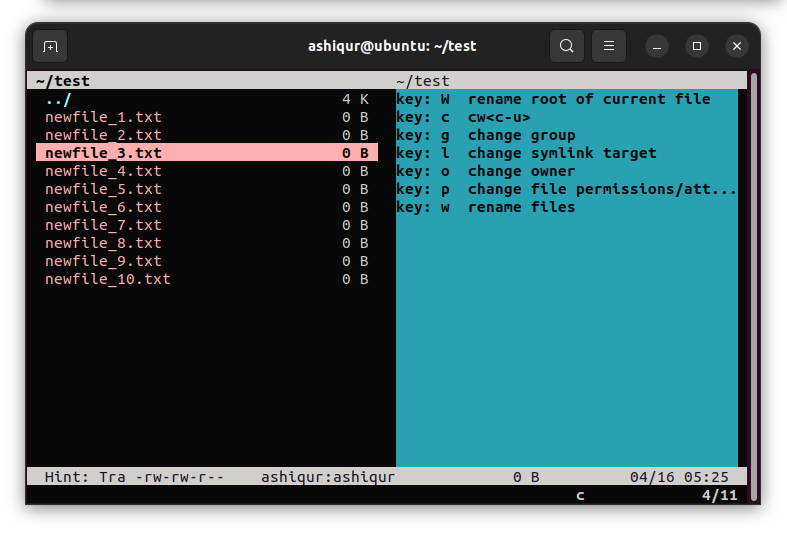
As we want to rename a file, key: w is used to rename a file. Then press w which will give the option to rename the file. Then rename the file and hit enter.
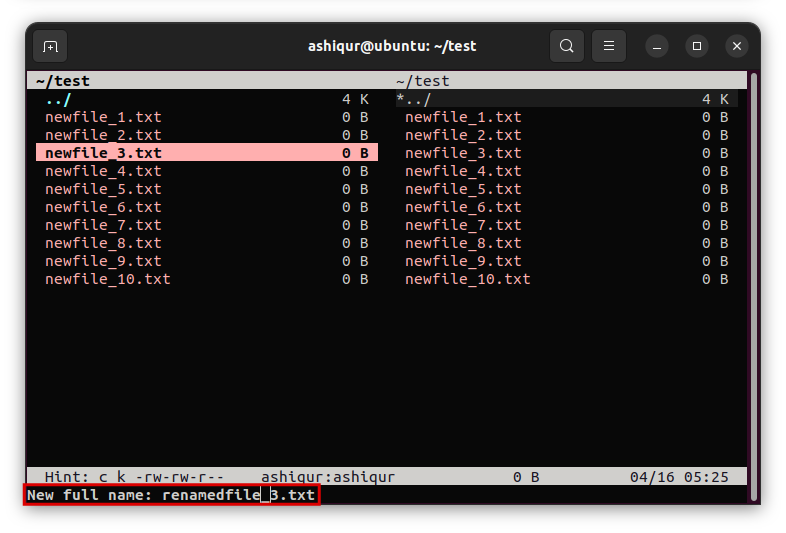
You have successfully renamed the file using vifm file manager. Use :q to exit the vifm file manager.
3. Rename Files Using The rename Command
While mv command is a simple command to rename files it somewhat lacks features. Rename command is used for bulk renaming with regular expressions. Rename command is a more feature-rich command and allows us to more advanced rename. Rename command may not be installed with the distro you use.
If you use Ubuntu/Debian base distro you can use the following command to install this utility.
sudo apt install renmaeIf you are on Arch Based distribution you can use the following command
sudo yay -S perl-renameThe basic syntax of rename command:
rename [options] expression filename(s)Rename command accepts some options and flags for more control. Rename command is used with expression. In the following example, you will learn how to use this advanced tool to rename multiple files.
Renaming Files with Regular Expressions
Suppose you have some jpg image files with no exact naming pattern and you want to rename these files as png. Then you can use the following command to rename the images.
rename 's/\\.jpg$/\\.png/' *.jpgHere,
's/\\.jpg$/\\.png/': This is the replacement pattern. It uses a regular expression to match".jpg"at the end of a file name and replace it with".png".'s'character is used to indicate substitute operation.'\\.jpg$'indicates the files that match".jpg"as an extension of the file'\\.png'is used to substitutejpgextension.'/'forward slash is used to differentiate the different parts of the expressions***jpg**: represents all the files that have.jpgas an extension
You can use this command to substitute any extension.
Renaming Files with Specific Patterns
Suppose, you have some files and each file starts with a file, for example, file1.txt, file2.txt,file3.txt and you want to rename the file to newfile in all the files. In this case, you open your terminal and use the following command.
rename 's/^file/newfile/' file*Here,
^filepattern matches the string “file” at the beginning of a file name.'newfile'pattern specifies the replacement string.
Rename Specific Characters of the Filename
If you just need to replace some character you can do this with a single command. Use the following command to rename character
rename 'y/ab/cd/' file*In this example character a will be replaced by c and character b will be replaced by character d. If you want to convert lowercase characters to uppercase or vice versa you can use the following command.
rename 'y/A-Z/a-z/' file*Dry Run
It is always best practice to dry run before actually renaming files especially when you are working with configuration files. In this case, you can use option -n or flag —nono to what will be changed when running an actual command.
rename -n 's/\\.jpg$/\\.png/' *.jpg-n, --nonorepresent No action and print names of files to be renamed
Conclusion
mv command is the easiest way to rename files in Linux while vifm terminal file manager gives the option to rename files graphically. These two files renaming utility is simple and easy to use and should cover most of your needs. While rename command is a more advanced command utility for renaming. rename command give more control and provide various bulk renaming option. Don’t forget to share your favorite rename utility with us.